Do Cardinal Fish Lay Eggs?
Yes, cardinal fish lay eggs. The male takes on the role of mouthbrooding to ensure the eggs' survival, protecting them from predators and providing an oxygen-rich environment.
This behavior, alongside intricate mating rituals, enhances the chance of successful fertilization and offspring survival. The male aerates the eggs constantly, ensuring excellent development.
This evolutionary strategy highlights the intricate parental care dynamics in these fish. As the eggs develop, you'll notice the eyes becoming visible, indicating readiness for fry emergence.
To fully understand their reproductive behavior and breeding challenges, there's much more to discover.

Key Takeaways
- Cardinal fish lay eggs, which are then mouthbrooded by the male for protection and oxygenation.
- The male performs courtship displays and tandem swimming to attract a female for mating.
- After mating, the male guards and cares for the eggs in his mouth until they hatch.
- The eggs develop in the male's buccal cavity, ensuring an optimal environment for growth.
- Proper water conditions and nutrition are crucial for the survival of the fry after they emerge.
Cardinal Fish Reproduction
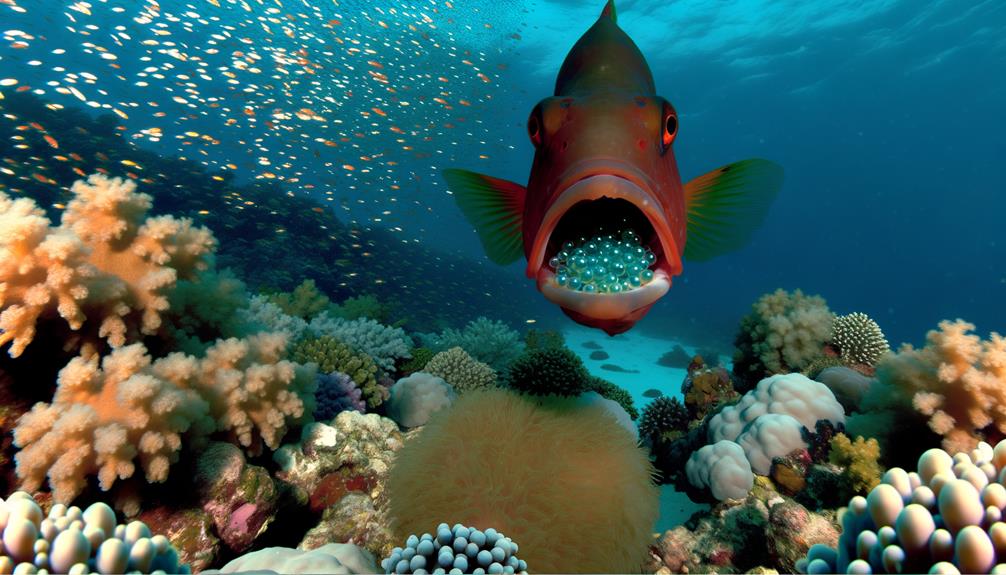

Cardinal fish reproduction involves a fascinating process of mouthbrooding, where the male carries fertilized eggs in his mouth until they hatch. You'll find that this method guarantees higher survival rates by protecting the eggs from predators. The male's buccal cavity provides a safe, oxygen-rich environment.
Scientific studies indicate that this form of parental care significantly enhances the chances of egg survival, reducing mortality caused by environmental threats. It's a clear example of evolutionary adaptation aimed at maximizing offspring viability. Additionally, mouthbrooding allows the male to control the developmental environment closely, ensuring ideal conditions.
Mating Rituals
During the mating process, male cardinal fish perform intricate courtship displays to attract females and secure a mate. You'll observe the males exhibiting conspicuous behaviors such as rapid fin movements and vibrant color changes. These displays serve to demonstrate the male's fitness and genetic quality.
Scientific evidence shows that females prefer males with more dynamic and frequent displays, selecting for traits that guarantee offspring survival. Additionally, males often engage in a behavior called 'tandem swimming,' where they closely follow the female, mirroring her movements. This synchronized swimming not only solidifies the pair bond but also signals the male's readiness to engage in the subsequent phases of reproduction.
Egg Laying Process
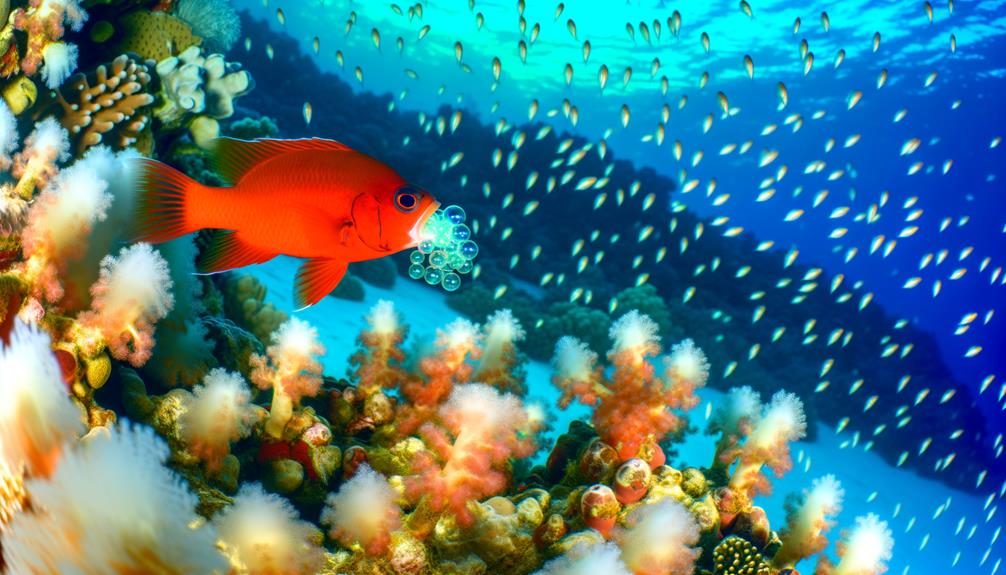

You'll observe that cardinal fish engage in intricate mating and courtship behaviors prior to egg laying, essential for ensuring successful fertilization.
During this process, males often exhibit territorial defense and signaling displays to attract females.
Post-fertilization, the male typically assumes parental care, mouthbrooding the eggs to protect them from predators and environmental hazards.
Mating and Courtship Behavior
Have you ever wondered how cardinal fish engage in their intricate mating rituals and egg-laying process?
During courtship, males display vibrant colors to attract females, swimming in a synchronized dance. Females select mates based on these displays, ensuring genetic importance.
Once paired, the female deposits eggs, which the male immediately fertilizes. This process, known as external fertilization, involves the male taking the eggs into his mouth for incubation.
The mouthbrooding behavior is crucial for the protection and oxygenation of the eggs. Studies show that this method increases the survival rate of the offspring, highlighting the evolutionary advantage of such behavior.
Understanding this process provides insight into the complex reproductive strategies of cardinal fish, emphasizing their adaptive success in aquatic environments.
Parental Care Dynamics
The mouthbrooding behavior of male cardinal fish exemplifies a unique form of parental care, where the male not only incubates the eggs but also promotes their ideal development by constantly aerating them within his buccal cavity. You observe this dynamic unfold as the male takes the fertilized eggs into his mouth, ensuring they receive peak oxygen levels. This method minimizes predation risks and environmental stresses.
| Stage | Male Role | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Egg Incubation | Mouthbrooding | Protects from predators |
| Aeration | Constant mouth movement | Maximizes oxygenation |
| Hatching | Releases fry | Allows safe emergence |
This intricate process highlights a sophisticated evolutionary strategy, showcasing the male's critical investment in offspring survival. You can't help but admire how nature has crafted such an elaborate, effective parental care system.
Male Brooding
Male brooding in cardinal fish involves the male carrying and protecting the fertilized eggs in his mouth until they hatch. You'll find this behavior fascinating as it exemplifies a unique form of paternal investment.
The male's buccal cavity provides a safe environment, shielding the eggs from predators and environmental stress. Studies show that male brooding increases egg survival rates significantly. It's a strategic adaptation ensuring the propagation of their genes.
During brooding, males can't eat, demonstrating their commitment. This behavior illustrates an evolutionary trade-off: the male sacrifices his immediate nutritional needs for the future success of his offspring.
You'll appreciate the intricate balance of survival and reproduction in this extraordinary example of parental care.
Egg Development
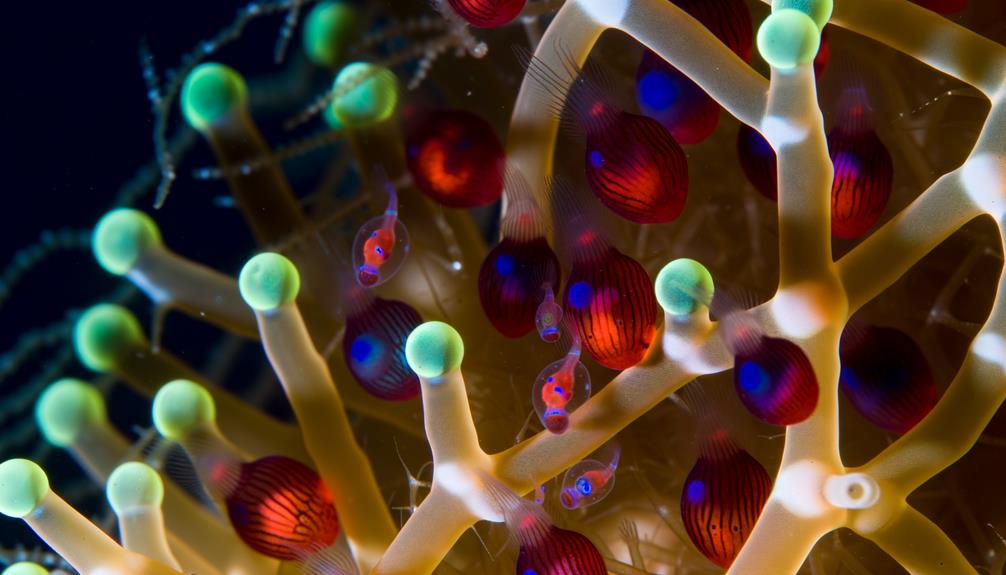
Throughout egg development, cardinal fish embryos benefit from the controlled environment provided by the male's buccal cavity, where ideal temperature and oxygen levels are carefully maintained. You'll find that this unique brooding behavior enhances that the embryos are protected from environmental fluctuations and potential predators. The male's buccal cavity offers a sanctuary where nutrient absorption and waste expulsion are optimized, fostering rapid and healthy development.
| Development Stage | Temperature (°C) | Oxygen Level (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cleavage | 25 | 7.5 |
| Gastrulation | 26 | 7.8 |
| Organogenesis | 27 | 8 |
| Growth Phase | 27.5 | 8.2 |
| Pre-Hatching | 28 | 8.5 |
This controlled environment significantly enhances the survival rate and overall fitness of the offspring.
Hatching Period
You should monitor the cardinal fish's eggs closely as the incubation period typically lasts between 18 to 30 days, influenced by water temperature and environmental conditions.
You'll observe the fry emerging when their yolk sacs are nearly depleted, indicating they're ready to swim independently.
Consistent observation allows you to identify these precise developmental milestones, ensuring best care for the newly hatched fry.
Incubation Timeframe Details
During the incubation period, cardinal fish eggs typically take around 20 to 25 days to hatch, depending on water temperature and environmental conditions.
You'll find that lower temperatures tend to prolong the incubation, while warmer conditions expedite the process. Best temperature ranges from 25°C to 28°C, improving embryonic development.
Salinity levels also play a significant role; maintaining consistent salinity guarantees successful hatching. Parental care is crucial, as male cardinal fish carry the eggs in their mouths, providing protection and oxygenation.
Empirical studies indicate that minimal disturbances during this period are essential. Monitoring water quality, including ammonia and nitrate levels, directly influences hatching success. Therefore, understanding these variables empowers you to facilitate a thriving breeding environment.
Fry Emergence Signs
As the incubation period concludes, careful observation reveals key signs indicating the imminent emergence of cardinal fish fry. You'll notice increased activity within the male's buccal cavity where the eggs are incubated. Look for subtle mouth movements as he aerates the eggs more frequently. The fry's eyes become visible through the egg membrane, signaling advanced development. Additionally, the male may exhibit heightened protective behavior, warding off potential threats near the nest.
| Sign | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Mouth Movement | More frequent aeration of eggs | Imminent hatching |
| Visible Fry Eyes | Eyes visible through egg membrane | Advanced developmental stage |
| Protective Behavior | Male warding off threats | Readiness to release fry |
These signs collectively indicate the approaching fry emergence, marking a critical phase in the reproductive cycle.
Fry Care

Proper fry care for cardinal fish involves maintaining best water conditions and providing a diet rich in nutrients to support healthy growth and development. You should keep the water temperature between 78-82°F and maintain a pH level of 8.1-8.4. Ammonia and nitrite levels must be zero, while nitrate should remain below 20 ppm.
Feeding the fry high-quality, finely ground foods like baby brine shrimp or specialized fry food guarantees they receive adequate protein and essential fatty acids. Frequent, small feedings are preferable to avoid overfeeding and water pollution.
Regular water changes, approximately 10-20% weekly, are essential to maintaining water quality. Using gentle filtration will prevent fry from being sucked into the filter, assuring their safety and promoting prime development.
Breeding Challenges
Breeding cardinal fish presents several challenges, primarily due to their specific environmental needs and the delicate nature of their offspring.
You'll need to create a stable aquarium environment, maintaining precise water conditions and temperature.
The offspring themselves are extremely sensitive, requiring specialized care to guarantee survival.
Consider the following breeding challenges:
- Water Quality: Cardinal fish larvae are highly susceptible to poor water conditions, requiring vigilant monitoring and frequent water changes.
- Feeding: Providing appropriate, nutrient-rich food for the larvae is essential, yet challenging, as they need microscopic live foods.
- Tank Setup: Ensuring a stress-free environment with plenty of hiding spots and minimal disturbances is essential for successful breeding.
Conclusion
So, after all this talk about cardinal fish reproduction, you might think they'd follow the usual fishy script. But no, it's the male that winds up doing the heavy lifting, brooding the eggs in his mouth. Isn't it ironic?
While the female gets to lay the eggs and swim off, you're left pondering how these males multitask so efficiently. After all, who knew the secret to successful reproduction was male mouthbrooding?
Nature's got quite the sense of humor.






